Difference Between Autotrophic and Heterotrophic Nutrition
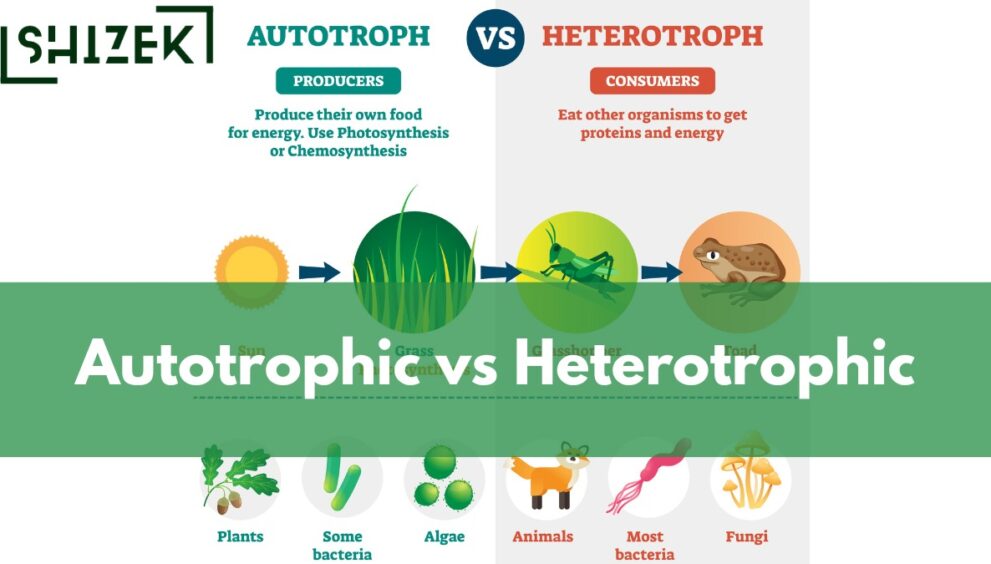
Nutrition is the process by which living organisms obtain and utilize food to meet their metabolic needs. Autotrophic and heterotrophic nutrition are two fundamental modes of nutrition that differ in their approach to acquiring food. While autotrophs can produce their own food through photosynthesis, heterotrophs rely on external sources for their nutrition. Understanding these two types of nutrition is essential to grasp the diversity of life on Earth.
Table of Content
- Difference Between Autotrophic Nutrition and Heterotrophic Nutrition
- What is Autotrophic Nutrition?
- What is Heterotohic Nutrition?
- Key Differentiate Between Autotrophs and Heterotrophs
What is the Difference Between Autotrophic Nutrition and Heterotrophic Nutrition?
| Parameter | Autotrophic Nutrition | Heterotrophic Nutrition |
| Mode of Nutrition | Produces own food using inorganic sources | Depends on consuming pre-formed organic matter from other organisms |
| Energy Source | Sunlight, photosynthesis | Chemical energy from consumed organic matter |
| Food Preparation | Uses chlorophyll to convert CO2 and water into glucose | Breaks down complex organic compounds through digestion and cellular respiration |
| Examples | Plants, algae, certain bacteria | Animals, fungi, most bacteria |
| Nutrient Dependence | Relatively independent of external food sources | Dependent on external sources for nutrition |
| Metabolic Pathways | Primarily photosynthesis | Digestion followed by cellular respiration |
| Carbon Source | Carbon dioxide from the atmosphere | Organic carbon compounds from consumed food |
| Role in Ecosystem | Primary producers, the foundation of the food chain | Consumers, rely on autotrophs for sustenance |
What is Autotrophic Nutrition?
Autotrophic nutrition is a type of nutrition in which an organism is able to produce its own food using simple inorganic substances such as carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight.
This process is also known as photosynthesis and is mainly found in plants, algae, and some bacteria.
During photosynthesis, the energy from sunlight is used to convert carbon dioxide and water into oxygen and glucose, which is then used as a source of energy by the organism.
Autotrophic nutrition is an important process that helps to sustain life on Earth by producing oxygen and providing a source of food for other organisms.
Note: The organisms that produce their own food are called Autotrophs.
Types of Autotrophs
- Photoautotrophs: These organisms use sunlight as their energy source and carbon dioxide as their carbon source.
- Examples of photoautotrophs include plants, algae, and certain types of bacteria that perform photosynthesis.
- Chemoautotrophs: These organisms use chemical energy from inorganic compounds as their energy source and carbon dioxide as their carbon source.
- Certain types of bacteria and archaea are examples of chemoautotrophs that perform chemosynthesis.
What is Heterotrophic Nutrition?
Heterotrophic nutrition is a type of nutrition in which organisms obtain their food by consuming other living things or organic matter. Unlike autotrophs, which produce their own food, heterotrophs cannot synthesize organic compounds from inorganic sources and must rely on other organisms for their nutrition.
Types of Heterotrophic Nutrition
- Holozoic nutrition: This involves the ingestion of solid or liquid organic food by an organism that is then broken down and digested internally. Examples of organisms that use holozoic nutrition include animals and fungi.
- Saprotrophic nutrition: This involves the extraction of nutrients from dead organic matter by decomposers such as fungi and bacteria. These organisms break down the organic matter externally and absorb the nutrients that are released.
- Parasitic nutrition: This involves the consumption of living organic matter by a parasitic organism, which feeds on its host. Examples of organisms that use parasitic nutrition include ticks, lice, and tapeworms.
Note: Organisms that cannot produce their own food and instead rely on consuming other organisms for energy and nutrients are called heterotrophs.
Types of Heterotrophs
- Herbivores: These are animals that mainly eat plants or plant-based materials.
- Examples include cows, rabbits, and deer.
- Carnivores: These are animals that mainly eat other animals.
- Examples include lions, tigers, and wolves.
- Omnivores: These are animals that eat both plants and animals.
- Examples include humans, bears, and pigs.
- Detritivores: These are organisms that obtain their food by feeding on dead organic matter.
- Examples include earthworms, vultures, and some types of bacteria.
- Parasites: These are organisms that obtain their food by living on or inside another organism, known as the host.
- Examples include ticks, fleas, and tapeworms.
- Fungi: These are organisms that obtain their food by absorbing nutrients from dead or decaying organic matter. They are decomposers and play an important role in breaking down organic matter.
Key Difference Between Autotrophs and Heterotrophs
- Autotrophs can synthesize their own nutrients, while heterotrophs cannot.
- Autotrophs are producers, while heterotrophs are consumers in the food chain.
- Autotrophs use inorganic sources like carbon dioxide as their carbon source, while heterotrophs use organic carbon compounds.
- Autotrophs can be photoautotrophs (using sunlight) or chemoautotrophs (using chemical energy), while heterotrophs rely on organic compounds produced by other organisms.
- Autotrophs include plants, algae, and certain bacteria, while heterotrophs include animals, fungi, most bacteria, and some protists.